Има голяма разлика между двигател и електрически двигател. Днес ще разгледаме някои от разликите между двата вида двигатели и ще ги разграничим по-подробно.
Какво е електрически двигател?
Електродвигателят е електромагнитно устройство, което преобразува или предава електрическа енергия съгласно законите на електромагнитната индукция.
Двигателят е представен с буквата M във веригата (D в стария стандарт) и основната му функция е да произвежда задвижващ въртящ момент като източник на енергия за уреди или различни машини, докато генераторът е представен с буквата G във веригата и основната му функция е да преобразува електрическата енергия в механична енергия.
一. Деление и класификация на двигателите
1. Според вида на работещото захранване: може да се раздели наDC мотори променливотоков двигател.
2. Според структурата и принципа на работа, може да се раздели наDC мотор, асинхронен двигател и синхронен двигател.
3. Според режима на стартиране и работа: еднофазен асинхронен двигател с кондензаторно стартиране, еднофазен асинхронен двигател с кондензаторно захранване, еднофазен асинхронен двигател с кондензаторно стартиране и работа и еднофазен асинхронен двигател с разделена фаза.
4. Според предназначението, двигателят може да бъде разделен на: двигател за задвижване и двигател за управление.
5. Според структурата на ротора: асинхронен двигател с клетка (по стар стандарт се нарича асинхронен двигател с клетка на катерици) и асинхронен двигател с навит ротор (по стар стандарт се нарича асинхронен двигател с навит ротор).
6. Според скоростта на работа, те могат да бъдат разделени на: високоскоростни двигатели, нискоскоростни двигатели, двигатели с постоянна скорост и двигатели с регулиране на скоростта. Нискоскоростните двигатели се разделят на зъбни двигатели, електромагнитни редукторни двигатели, моментни двигатели и синхронни двигатели с лапа-полюсен механизъм.
二Какво е електрически двигател
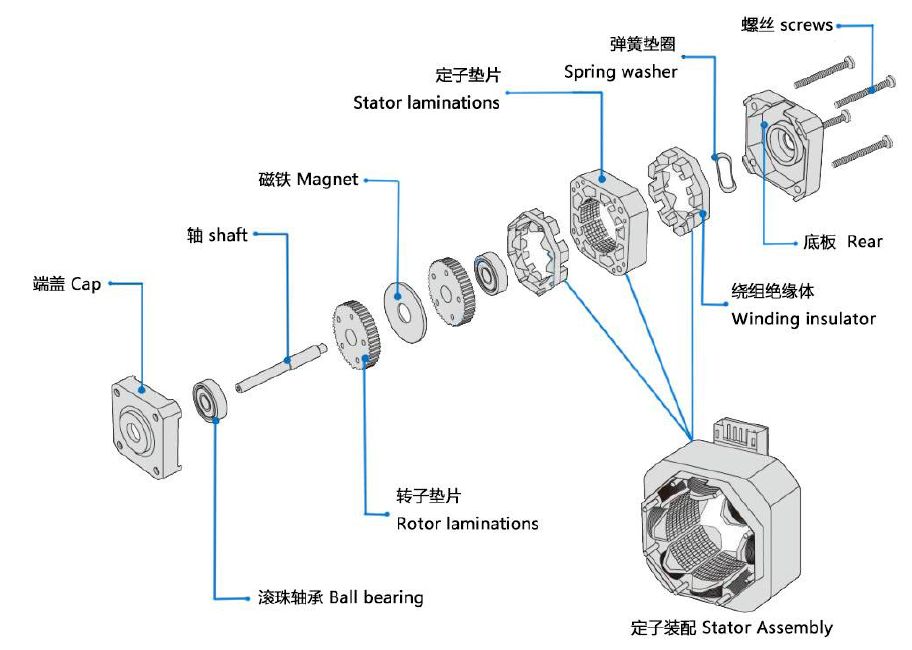
Електродвигателят (мотор) е устройство, което преобразува електрическата енергия в механична. Това е използването на захранвани бобини (известни също като статорни намотки) за генериране на въртящо се магнитно поле и въздействие върху ротора (като например затворена алуминиева рамка с клетка на катерици), за да се образува магнитоелектрическа енергия и въртящ момент. Електродвигателите се разделят наDC двигателии променливотокови двигатели според използвания източник на захранване. Повечето електрически двигатели в енергийните системи са променливотокови двигатели, които могат да бъдат синхронни или асинхронни (скоростта на магнитното поле на статора на двигателя и скоростта на въртене на ротора не поддържат синхронна скорост). Електродвигателят се състои главно от статор и ротор. Посоката на движение на захранван проводник в магнитно поле е свързана с посоката на тока и посоката на линиите на магнитната индукция (посока на магнитното поле). Принципът на работа на двигателя е, че магнитното поле действа като сила върху тока, карайки двигателя да се върти.
Накратко, Основната структура на електрическия двигател
1. Структурата на трифазен асинхронен двигател се състои от статор, ротор и други аксесоари.
2. DC двигателят има осмоъгълна, изцяло ламинирана структура със последователна възбуждаща намотка, която е подходяща за технология за автоматично управление, където се изисква въртене напред и назад. Те могат да бъдат изработени и със последователно възбуждащи намотки според изискванията на клиента. Двигателите с централна височина от 100 до 280 мм нямат компенсационна намотка, но двигателите с централна височина от 250 мм и 280 мм могат да бъдат изработени с компенсационна намотка според специфичните условия и нужди, а двигателите с централна височина от 315 до 450 мм имат компенсационна намотка. Размерите и техническите изисквания на двигателите с централна височина от 500 до 710 мм са в съответствие с международните стандарти IEC, а механичните размерни допуски на двигателите са в съответствие с международните стандарти ISO.
Има ли някаква разлика между двигател и електрически двигател?
Електродвигателите включват както двигатели, така и генератори. Това е общ термин за генератори и двигатели, като концептуално двата понятия се различават по тази разлика. Електродвигателят е само един от режимите на работа на двигателя, но той работи в електрически режим, което означава, че електрическата енергия се преобразува в други форми на енергия; другият режим на работа на двигателя е генератор, който работи в режим на генериране на енергия, преобразувайки други форми на енергия в електрическа енергия. Някои двигатели, като например синхронните двигатели, обаче обикновено се използват по-често като генератори, но могат да се използват и директно като електродвигатели. Асинхронните двигатели се използват по-често като електродвигатели, но с добавянето на прости периферни компоненти могат да се използват и като генератори.
Време на публикуване: 14 август 2023 г.